Let us get one thing straight: there is no ONE universally applicable list of a PMO’s functions and responsibilities. The PMO functions and their prioritization always depend on the type of project the project management office (PMO) is expected to manage in a multi-project environment. At the same time, they also depend on the individual objectives you would like to achieve with your PMO. This article provides an overview of many possible project management office functions.
In the extensive PMO survey conducted by TPG The Project Group in 2020, we also asked about PMO functions. The results show how often PMOs are engaged in which of the six areas of responsibility and how well established these individual areas are at the respondents’ companies. This provides you with a good comparison as well as ideas for functions you could consider next for your PMO.
In addition, you will find chapters on PMO manager tasks and necessary skills as well as possible PMO roles at the end.
The article covers the following topics:
- PMO areas of responsibility
- Results regarding PMO responsibilities from the TPG PMO Survey
- Area of responsibility 1: Standardization of methods, processes and tools
- Area of responsibility 2: Training / coaching
- Area of responsibility 3: Project implementation
- Area of responsibility 4: Multi-project management
- Area of responsibility 5: Resource management
- Area of responsibility 6: Strategic support
- What are PMO manager tasks and necessary skills?
- Possible PMO roles
- What makes a good PMO?
- Conclusion – PMO functions
Let us start.
PMO Areas of Responsibility
A PMO is a permanent organizational unit that is centrally responsible for all projects within a company or a department in the context of multi-project management. Depending on the level of project management maturity at the company, PMO functions can vary greatly.
The functions can be quite simple in the beginning, for instance filing status reports. The other extreme is a PMO taking on strategic responsibilities. This will be the case once top management has come to value the support of its own PMO, e.g., in the preparation of strategic portfolio decisions.
Regardless of the current PMO functions: in our opinion, a PMO is a service provider dedicated to giving its stakeholders the good feeling of being in full control of all projects.
PMO functions often include the control of activities and data. However, this should not bring forth a kind of “project police”. Rather, the goal should be to create trust with a view to maximizing the success of the projects and the stakeholders’ satisfaction with the PMO.
Our tip: Make sure your PMO is not seen as the “project police” but focuses on the satisfaction of all stakeholders. This will strengthen the acceptance of all PMO activities.
Special Download (PDF): What are typical PMO Functions? (+ their importance)
This article provides you with a good comparison as well as ideas for functions you could consider next for your PMO. Please fill in the form to download.
* Required Fields | Data Protection
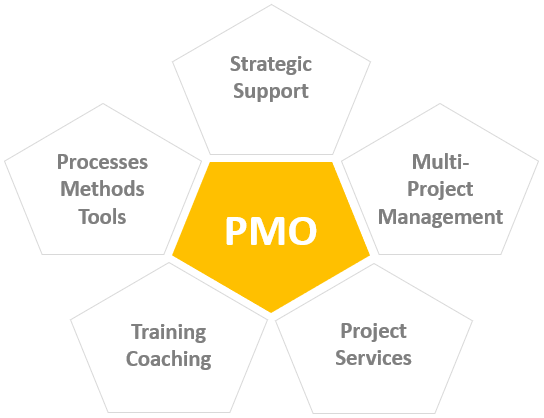
Possible areas of responsibility of the PMO are as follows:
- Strategic support (sPMO): Aligning project work with the corporate strategy by classifying, selecting, and prioritizing (and, if necessary, terminating) projects.
- Managing a multi-project environment / Resource management: This is the PMO’s primary function, and it includes maintaining a good overview of all the projects and ensuring that all the necessary data is always up to date and plausible. In this context, decisions regarding the scope, budgets and resources are prepared and made in due consideration of interdependencies between projects.
- Project implementation / services: This involves providing operational support in projects by taking on the management of a project, executing defined subtasks or providing project assistants.
- Training and coaching: Project managers and participants in the processes are trained and supported in the field. Possibly, career paths for project managers are offered.
- Methods, processes and tools: Choosing and adapting the PM methodologies and processes to best suit the needs of everyone involved at the company. Selection, implementation and management of appropriate tools for the different roles in project and portfolio management.
Tip: The Project Management Institute PMI® also provides a list of many PMO activities and insightful information on the PMO benefits in this article.
Special Download: 10 Vital PMO Success Factors (PDF file)
Please fill in the form.
* Required Fields | Data Protection
Results regarding PMO Functions from the PMO Survey
The results of the study are based on 330 comprehensive datasets from companies with a PMO in the DACH countries (i.e. Germany, Austria and Switzerland), that were collected in mid-2020. What makes it particularly fascinating is its comparison of low, high and top performers: what do top performers do better and what should latecomers focus on in particular? You will find more detail on the subject of PMO functions and many other results from the survey as well as important PMO tips in the TPG PMO Survey.
More detail about TPG’s extensive PMO Survey here (+ free download).
The survey assessed the different areas of responsibility and asked how well each of them was established. In addition, the participants were asked to estimate the current and future distribution of time spent on the different sets of responsibilities. This enabled us to generate an overview of PMO functions and planned changes regarding them.
Special Download: How to setup a PMO in 4 simple steps (PDF file)
Please fill in the form.
* Required Fields | Data Protection
The questions asked in this context were as follows:
- “How is your PMO’s annual workload distributed among these duties?”
- “How should your PMO’s annual workload be distributed among these duties going forward?”
The result (see chart below):
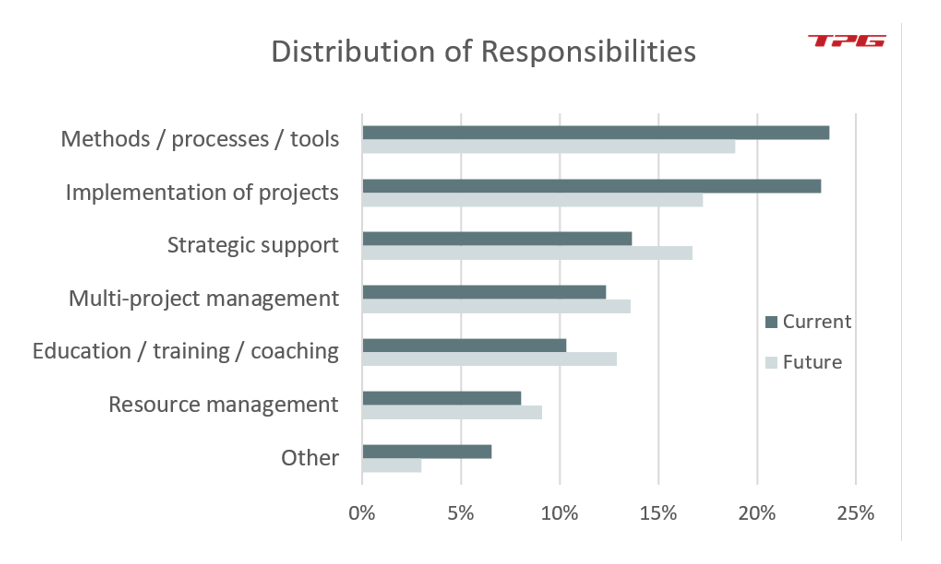
A quarter of all participants’ PMOs concerns itself most with the two areas “methods, processes and tools” and “implementation of projects”. “Resource management” plays the smallest part.
However, more time budget is intended to be taken up by “strategic support”, “multi-project management”, “training” and “resource management” in the future. To accommodate this, PMOs mean to reduce the time spent on “standardization” and “implementation of projects”.
In the following chapters, the PMO areas of responsibility are split into individual PMO functions. In each chapter, you will find a chart from the PMO Survey breaking down the results into four categories:
- “Well-established”
- “Implemented, but improvements are planned”
- “Start in 12 months”
- “Not planned”
This enables you to identify which PMO functions the companies perform to what intensity and how well-established they are according to the survey.
Where would you place yourself in the different charts?
Area of Responsibility 1: Standardization of Methods, Processes and Tools
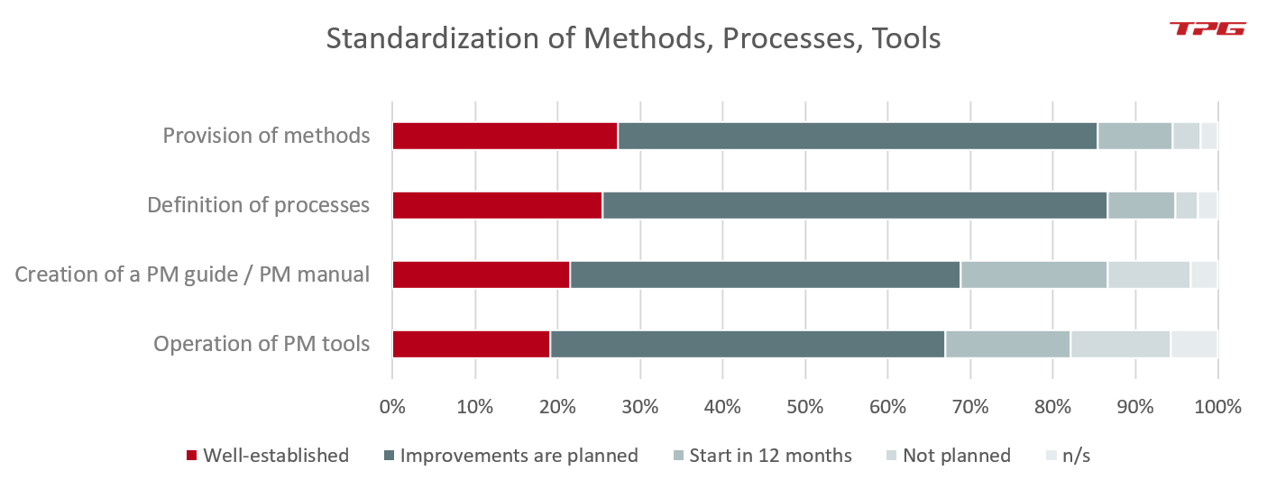
The standardization of the multi-project environment tends to be among the first responsibilities of any PMO. To obtain an overview of the project landscape, a centrally managed project list is an essential prerequisite. If you wish to create one, you will need methods such as the project order and the project status report from which the essential information must be transferred to the list.
Our tip: To keep the data up to date, you need appropriate processes in place. Your project managers and other stakeholders have to be able to understand and apply these, which is why a project manual or a PM guide should be available to all involved.
Therefore, the functions in this area of responsibility are at a minimum:
- Selection and provision of methods
- Definition and specification of processes
- Creation of a PM guide
- Selection and operation of suitable PM tools
Interested in finding out more about the tools? Read our article on PMO Tools.
Area of Responsibility 2: Training / Coaching
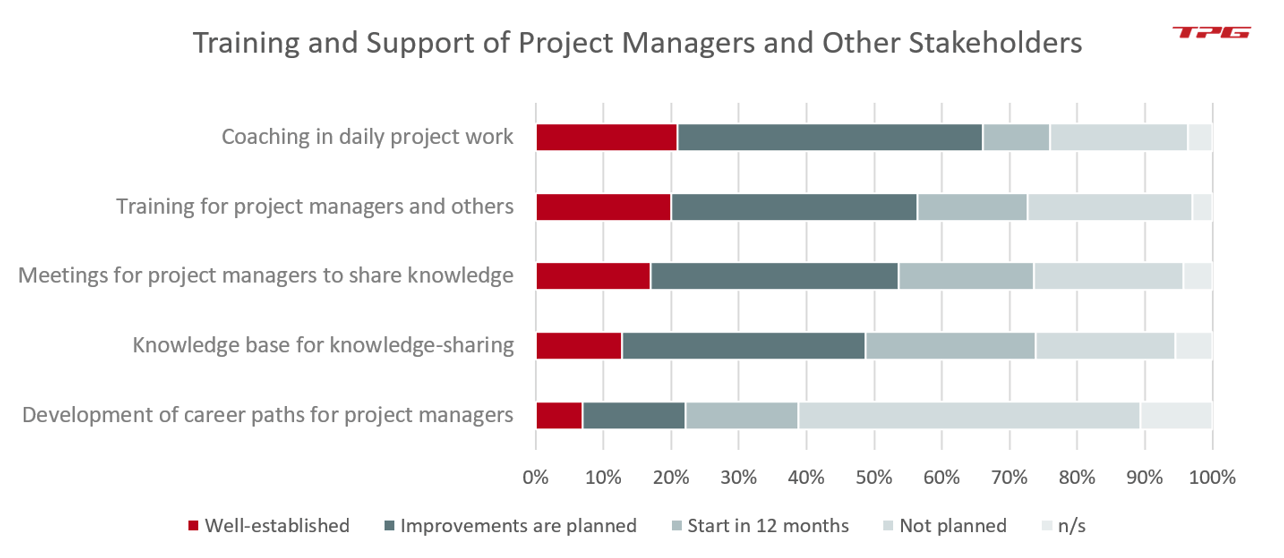
Since the establishment of methods, processes and tools includes their application by the staff, the PMO also has to provide the respective training and active fostering. This concerns qualifying your project managers and other stakeholders and providing further training of, and assistance in, daily project work. In this area of responsibility, we subsume the following PMO functions:
- Coaching in daily project work
- Training for project managers and others
- Meetings for project managers to share knowledge
- Maintaining a knowledge base for the stakeholders
- Development of career paths for project managers
Area of Responsibility 3: Project Implementation
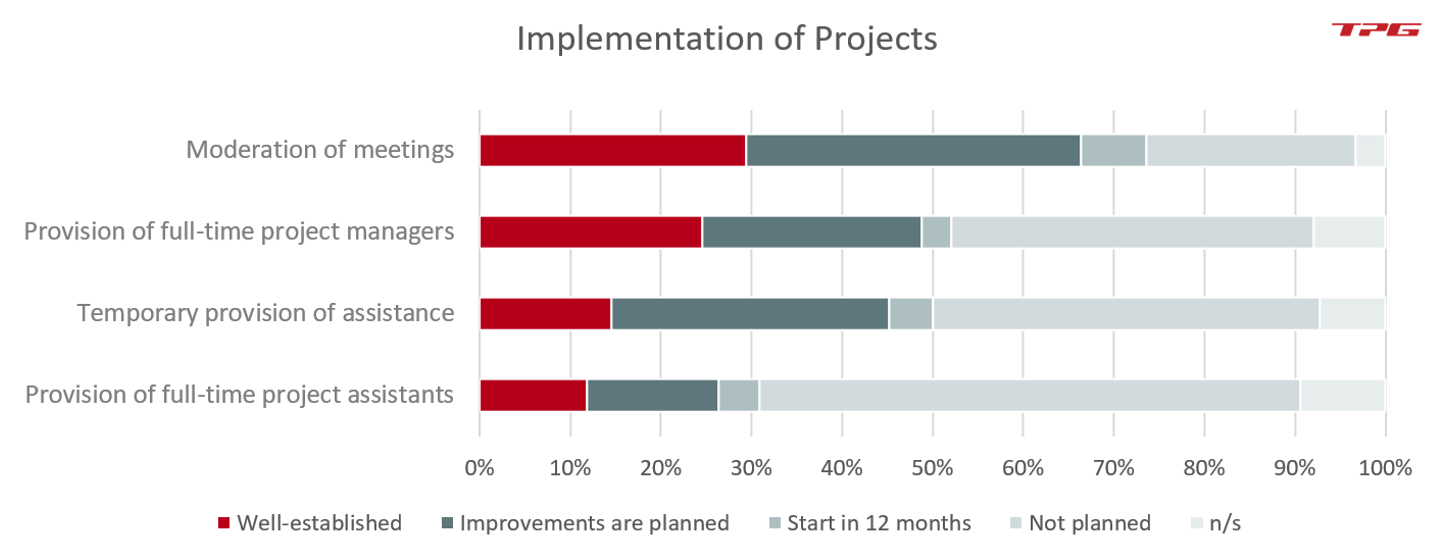
This concerns the operational support in projects headed by the organization and implementation of project-related meetings for moderation and coordination. Your PMO could also provide assistants and administer support for individual project management tasks. Another option would be to have a PMO member take on the role of project manager full-time. Full-time project managers tend to deliver better project results than individuals who only occasionally work as project managers. Therefore, possible PMO functions in this area could be as follows:
- Moderation of meetings
- Provision of full-time project managers
- Temporary provision of assistance
- Provision of full-time project assistants
Area of Responsibility 4: Multi-Project Management
With the functions in the area of multi-project management, your PMO is meant to create a clear overview of all projects and ensure the currency of the necessary data. You must provide stakeholders with valuable information so that they can make sound decisions. For this, you need to prepare and conduct project portfolio meetings properly.
Further reading: Why Have a PMO? Definition, Advantages and Added Value
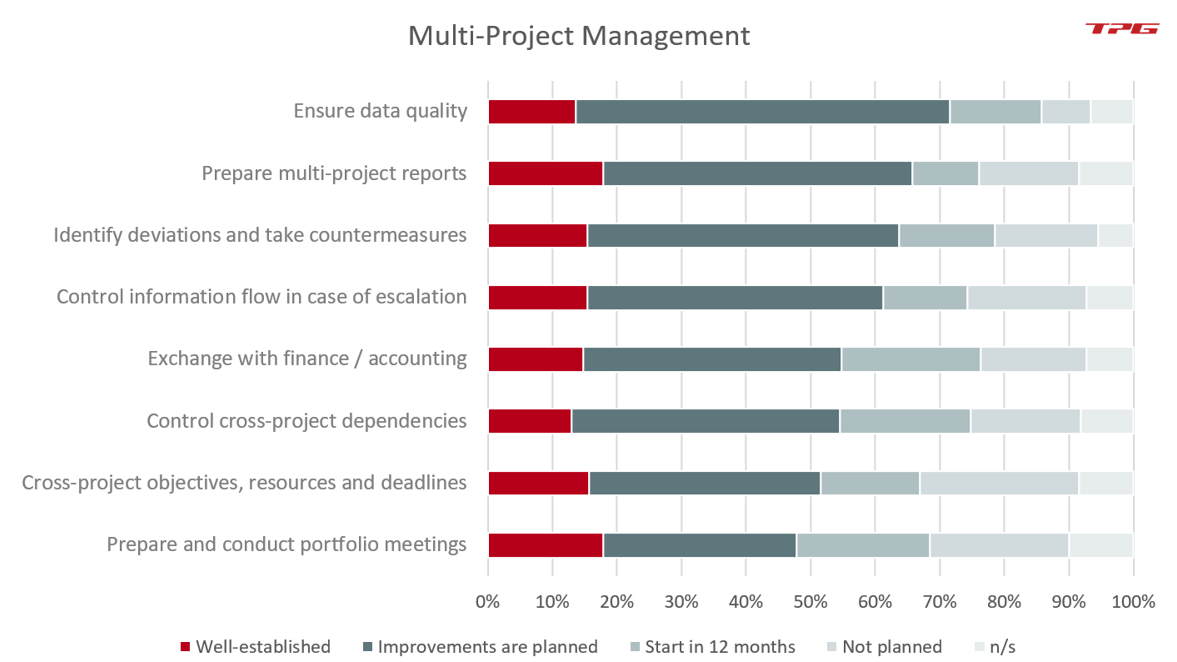
The topic of multi-project management and the regular activities involved is certainly one of the key responsibilities of the PMO. They include:
- Ensuring data quality
- Preparing multi-project reports
- Identifying deviations and taking countermeasures
- Controlling the flow of information in case of escalation
- Exchange with finance / accounting
- Controlling cross-project dependencies
- Overview of cross-project objectives, resources and deadlines
- Preparing and conducting portfolio meetings
Download now: Free eBook (PDF) on “The PPM Paradise”
Here is what an optimal customizable solution for project, portfolio and resource management (PPM) should be capable of – tips and important arguments for your decision-makers. > Download eBook (PDF) “The PPM Paradise”
Area of Responsibility 5: Resource Management
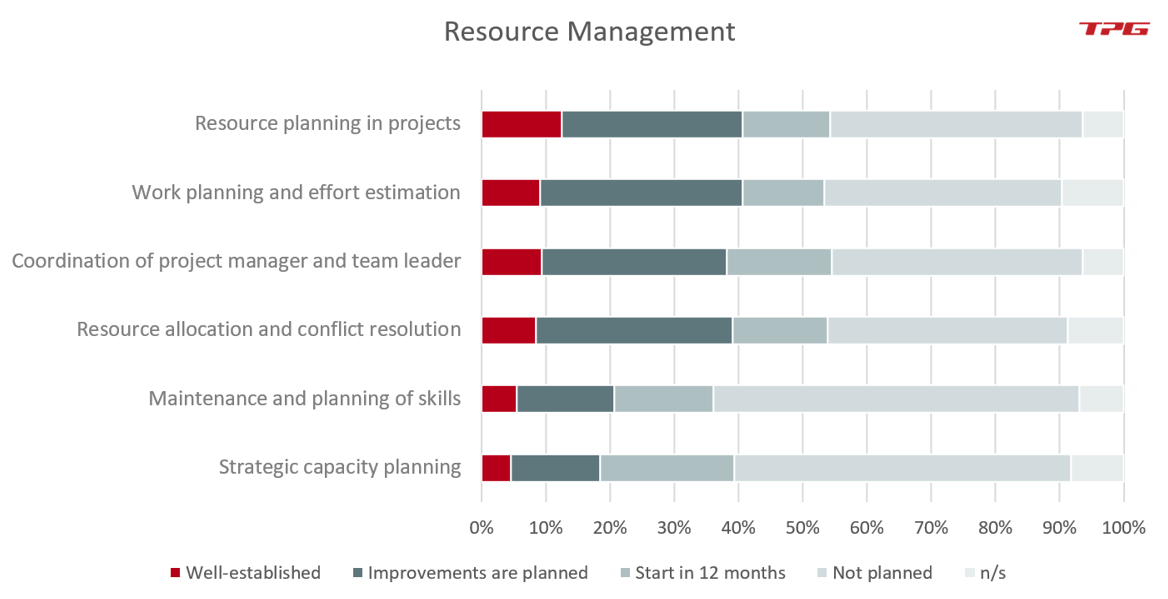
Of late, PMOs have increasingly given priority to the topic of resource management. In volatile times like these, resource management has become a real challenge at all levels. This topic concerns the support in strategic capacity planning, tactical resource planning between project and line managers as well as functional work planning.
As the PMO Survey has demonstrated, incorrect effort estimations are a frequent reason for unsuccessful projects. In this area, a PMO can contribute to the improvement of the results not only by selecting the right people for the projects but also by assisting with the effort estimation. There are many possibilities for your PMO to provide value in resource management. Such PMO functions include:
- Resource planning in projects
- Work planning and effort estimation
- Coordination of project manager / team leader
- Resource allocation and conflict resolution
- Maintenance and planning of skills
- Strategic capacity planning at portfolio level
Special Download: Capacity Planning – 4 Important Success Factors (PDF file)
Please fill in the form.
* Required Fields | Data Protection
Area of Responsibility 6: Strategic Support
Usually, PMOs only take on strategic support in the company once they have been around for several years. Our approach to this topic is different, however.
Our tip: Work on strategic topics as soon as possible. In our opinion, it makes more sense to improve the strategic decisions in the selection and prioritization of projects first, before you address the individual methods and processes in the ongoing projects. Pursuing the wrong projects properly is not a good option.
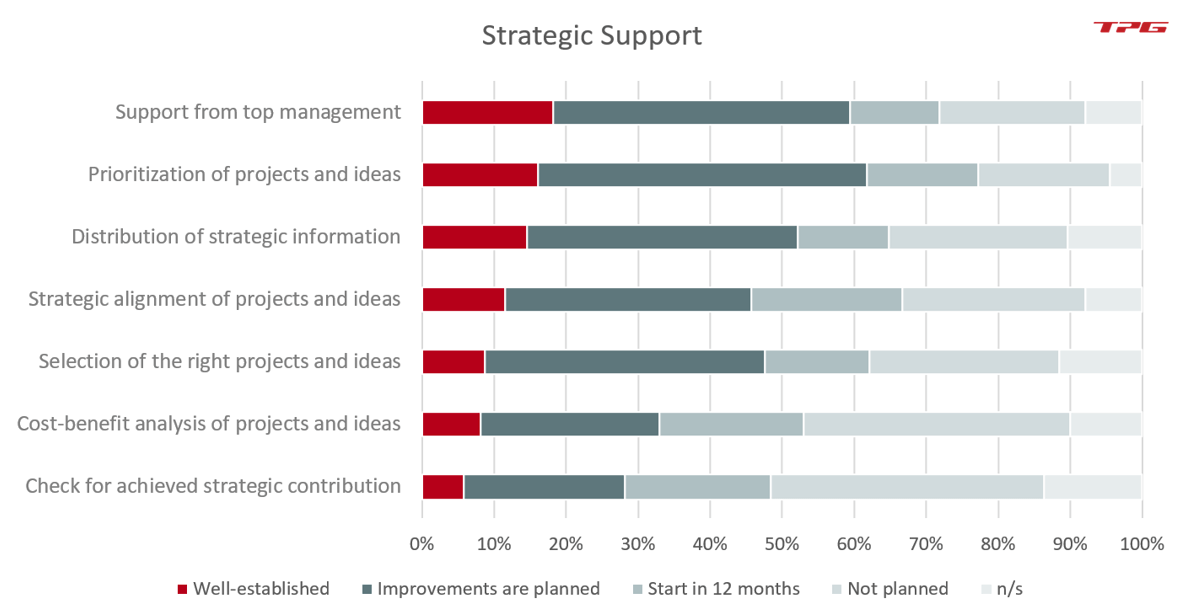
PMO functions in this strategic area can encompass:
- Support of top management
- Prioritization of projects and ideas
- Distribution of strategic information
- Strategic alignment of projects and ideas
- Cost-benefit analyses of projects and ideas
- Check for achieved strategic contribution
What Are PMO Manager Tasks and Necessary Skills?
Possible PMO manager tasks can be derived from the PMO functions described in the previous chapters and also depend on whether they can be mastered at the company concerned at this point in time. In addition, the tasks depend on the size of the PMO team. An important factor is also that the PMO manager does not usually have disciplinary authority and therefore needs support from the top (in certain cases there are very powerful department heads that are able to block things, also in relation to top management).
Important PMO manager tasks can be:
- Managing and optimizing the PMO
- Linking development / production and top management
- Supporting the project managers
- Building and expanding methodological competence and PM tools
- Reporting to top management
- Creating acceptance and transparency
- Ensuring data quality
- Finding appropriate tools
- Developing and structuring processes
- Preparing the steering board
- Ensuring the response rate (% of updated timesheets)
- Coaching project participants (encourage and challenge)
- Change management to establish tools and processes and their acceptance (impossible without backing from top management)
A PMO manager is sandwiched between the decision-maker level and the project manager level. The person needs to be able to handle this position and to hold their ground both upwards and downwards. In this context, the following PMO manager skills are necessary:
- Solution orientation and pragmatism
- Strong organizational skills
- Exceptional skills in dealing with the stakeholders
- Good leadership skills and empathy
- Critical thinking and attention to detail
- Ability to work under pressure
- Excellent oral and written communication skills
- Maturity and experience in the project environment (for sufficient standing)
- Assertiveness and diplomacy
- Sufficient financial knowledge
- Commercial thinking
Possible PMO Roles
Depending on the company, the organization of a PMO and its functions in the project environment can vary. If we assume a large PMO, the following PMO roles are conceivable, each with different responsibilities and functions:
- PMO Manager / Head of PMO: This position is the most important PMO role and has been described extensively in the previous chapter. It is responsible for the overall management and strategic direction of the PMO. Even with small PMOs, this role will always exist.
- PMO Member: This role supports the PMO Manager. It acts as an interface between the various project participants and contributes to the effective implementation of the project goals.
- Project Manager: This role can also be part of a PMO that “lends” its project managers to the projects. They are responsible for planning, monitoring and controlling individual projects over the course of their lifespan.
- Project Administrator: This PMO role supports project managers with documentation, reporting and meeting organization.
- Quality Manager: Their task is to ensure that all processes in the project environment and the results meet the defined quality standards.
What Makes a Good PMO?
A good PMO does everything to ensure smooth project implementation and control. It acts as a central hub for clear communication and coordination between different project teams. It ensures proven methods and processes are implemented to achieve project goals efficiently.
The ability to react to changes in a flexible way and a proactive risk management strategy are essential.
In addition, a good PMO plays a crucial role in the provision of meaningful data and reports to support informed decisions at all levels of the organization.
Overall, a good PMO is characterized by:
- Agility
- Clear communication
- Effective resource management
- Capacity for continuous improvement
Conclusion – Typical PMO Functions and Areas of Responsibility
The functions of a PMO can differ widely depending on the requirements of the company and the length of the PMO’s existence. This article has introduced you to the key areas of responsibility of the PMO listed again below and possible related individual functions:
- Area 1: Standardization of methods, processes and tools
- Area 2: Training / coaching
- Area 3: Project implementation
- Area 4: Multi-project management
- Area 5: Resource management
- Area 6: Strategic support
The extensive PMO Survey by TPG The Project Group has demonstrated that the most time is currently allocated to the PMO functions of standardization of methods, processes and tools as well as implementation of projects. According to the respondents, this focus is however supposed to shift in the future towards strategic functions and those in the areas of multi-project and resource management as well as training.
What is more, the PMO survey showed significant differences in the PMO functions between the performance levels of top, high and low performers. The differences were most pronounced with regard to the functions of supporting multi-project management and resource management as well as in individual areas of training and strategic support.
The lead of the top performers’ PMOs is most advanced when it comes to the following four PMO functions:
- Strategic capacity planning
- Managing the skills of staff members
- Provision of career paths for project managers
- Proof of strategic contribution of projects
Our final tips:
Get to know the individually adaptable “PPM Paradise” – the optimal environment for your enterprise-wide project, program, portfolio and resource management (PPM). Download the free eBook “The PPM Paradise” now (just click, no form).
And sign up for our bi-weekly blog newsletter with information on more hands-on articles, eBooks, etc. to improve your project management maturity level.
Where is the focus in the PMO functions of your company and how would you like to see it shift in the future? We look forward to receiving your comment below.
Subscribe to TPG BlogInfo: Never miss new practice-oriented tips & tricks
Every other week: Receive practical tips in TPG blog posts written by recognized experts in project, portfolio, and resource management.
* Required Fields | Data Protection
 Johann Strasser
Johann Strasser
Managing Partner at TPG The Project Group
The certified engineer has been a managing partner at TPG The Project Group since 2001. After many years as a development engineer in the automotive and energy sectors, Johann Strasser spent a decade as an independent trainer and consultant in the field of project management. During his tenure, he also served as project manager for software projects in the construction industry and provided scheduling and cost management support for large-scale construction projects. At TPG, he applies his expertise in product development and consulting services for international clients. His special focus is on PMO, project portfolios, hybrid project management, and resource management. For many years now, he has shared his knowledge through presentations, seminars, articles, and webinars.
 Achim Schmidt-Sibeth
Achim Schmidt-Sibeth
Senior Marketing Manager
After earning his engineering degree in environmental technology, he gained many years of experience in project management through his work at an engineering office, an equipment manufacturer, and a multimedia agency. Achim Schmidt-Sibeth and his team have been responsible for marketing and communication at TPG The Project Group for many years now.










4 Comments
Well, re-entering the PMO debate.
The large percentage of respondents who will address resource management in the next 12 months reminds me of my To Do lists.
One fundamental is to define the boundaries of project management and to obtain excellent feedback on how much of project managers’ effort is spent within those boundaries. Without this the PMO has no continually improving model. This is a topic with which I have been wrestling and am now joined by a few others.
Any wider interest is welcome.
Thank you for sharing your insightful thoughts and experience.
I am looking for some PMO related training, gating process, template, sponsor training (how to be a good sponsor for a project)
Hi Jing Ma, thank you for your comment! At TPG, we regularly offer PMO training (hybrid format, both on-site in Munich and virtual) in German language in our public seminar program. See dates here:
https://www.theprojectgroup.com/de/pmo-seminar-schulung-training
If you are interested in a training in English language and you are part of a group of colleagues with the same interest, it would be possible to organize a company seminar: https://www.theprojectgroup.com/en/pmo-training-seminar